
Money Supply Numbers Show the Fed is Making Headway
Money Supply, as reported by the Federal Reserve, fell by the largest amount ever recorded. This significant year-on-year drop shows the Fed’s tight monetary policy at work. However, despite the dramatic decline of cash available to consumers, the pace of increase that led up to the twelve-month period was even more dramatic. This indicates the Fed is not even close to finished draining liquidity from the economy, which serves to push up the cost of money (interest rates).
What is M2, how does it impact spending, and how much lower can the money supply go to reach “normal”? Let’s explore.
The M2 Report
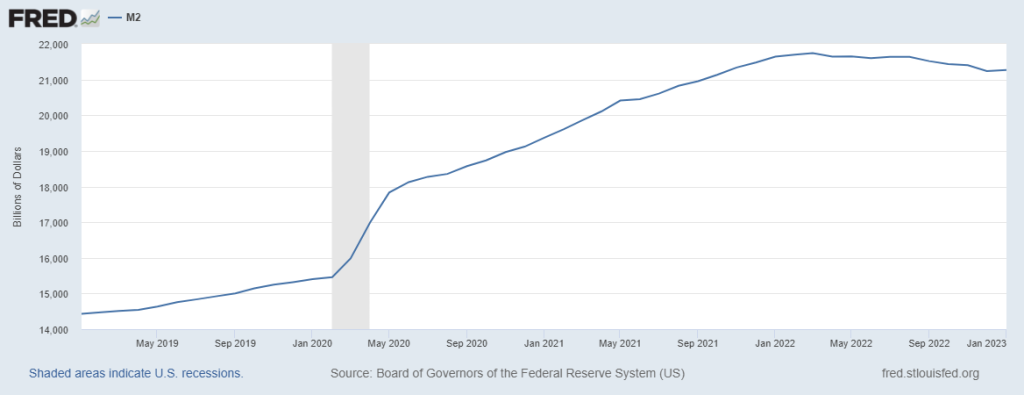
Data for January, released on February 28th, showed a negative growth rate of 1.7% versus a year ago. This is both the biggest yearly decline and also the first time ever it has contracted in consecutive months. The monthly rate of change has been falling consistently since mid-2021. As indicated on the chart below, it follows a historic peak of 27% growth in February 2021.
Money Supply is a measure of household liquidity, it includes household cash on hand, savings and checking deposits, and money market mutual funds. The level had been growing slowly, keeping pace with low inflation until 2020. In response to pandemic-related economic risks, the economy was then flooded with cash by the Fed. Like any other oversupply, this oversupply causes money’s value to decline – a recipe for inflation.
The Fed’s Actions
For almost a year, the Fed has been draining liquidity from the US economy. This includes the well-publicized retargeting of overnight bank lending rates which are accomplished by contracting the aggregate amount of cash banks hold in reserves. Draining liquidity also includes quantitative tightening by the Fed, not repurchasing maturing securities.
The Fed’s tightening is having an impact on savings and cash available to households. Although the consumer is still spending, the decline in savings makes the spending pace unsustainable. Unrelated to M2, but as important, is that consumer borrowing is up, and this, too, can not stay on an upward trajectory forever. The Fed’s actions have a lag time, but it is becoming obvious that there will come a point when consumers will need to change their spending habits downward. This is how inflation is expected to be reeled in, but it isn’t certain whether it is being reeled in at a pace where the Fed can succeed at reaching the 2% inflation rate goal – particularly in light of the last inflation number actually being higher than the previous month.
Where We Are Now
Although M2 growth rates declined at a pace shattering all records, levels are still abnormally high. To put numbers on it, Money Supply remains 39% higher than it was before the Covid-19 pandemic, just three years ago. In other words, the amount of liquidity in the economy is still significant, and too much money chasing too few goods and services lead to rising prices.
The current M2 of $21.27 trillion is nearly $6 trillion higher than the pre-pandemic level. At this point, money in the economy has surpassed real gross domestic product levels, a momentous shift that first happened in 2020 when the Fed flooded the economy with cash as the pandemic hit.
All of this indicates the Fed is actually being patient despite the dramatic tightening over the past year. It also makes it clear that they are not done mopping up the Covid-19 monetary mess. And investors shouldn’t be surprised to see their resolve continue until balances are more in-line with moderate inflation rates.
Take Away
The still elevated M2, despite its record yearly decline, is feeding inflation. The Fed is making headway removing fuel to the inflation fire.
However, consumers that historically have continued to spend at near unchanged levels, even when their disposable income no longer supports it, do eventually adjust. When this adjustment occurs, economic activity will slow. That’s when the Fed will be on the path to winning its inflation fight. Then perhaps we may actually get a pivot in monetary policy.
Managing Editor, Channelchek